Recycling of organic waste
Practical Action
combustion on an open fire to complex energy production processes that use this waste as a fuel
stock. It is not within the scope of this paper to deal with the many and varied uses of agricultural
residues.
Methods of processing organic waste
As mentioned in the introduction, there are three main ways in which organic waste can be used:
soil improvement
animal raising and
to provide a source of energy
Differing levels of processing are required for achieving the above and in this section we will take a
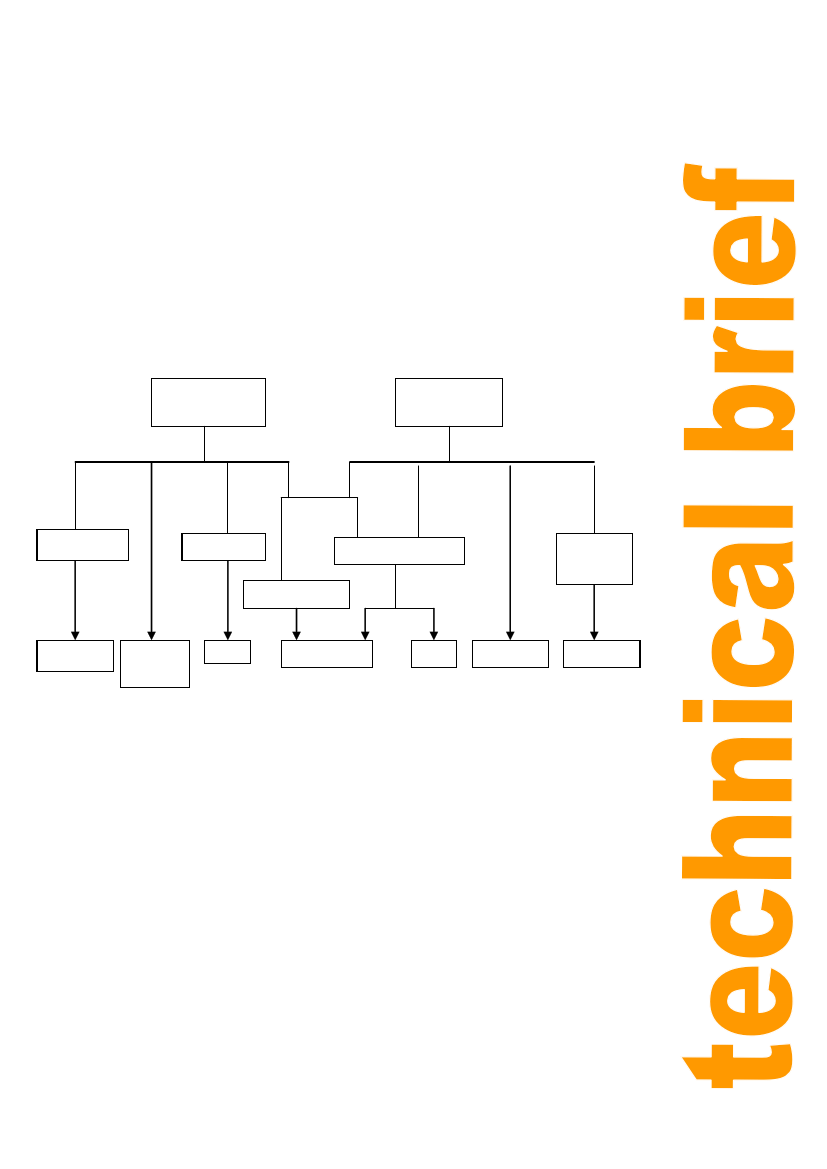
brief look at just some of the common approaches to using organic waste. Figure 2 below, shows
some of the options in the form of a flow diagram.
Urban organic/
vegetable waste
Human and
animal waste
Composting
Briquetting
Anaerobic digestion
Co-composting
Compost
toilets
Compost
Animal
feed
Fuel
Compost
Fuel Fertiliser
Compost
Figure 2: Processes and products from organic waste
Composting
Composting is simply the method of breaking down organic materials in a large container or heap.
The decomposition occurs because of the action of naturally occurring micro-organisms such as
bacteria and fungi. Small invertebrates, such as earthworms and millipedes, help to complete the
process. Composting can convert organic waste into rich, dark coloured compost, or humus, in a
matter of a few weeks or months. There is nothing mysterious or complicated about composting.
Natural composting, or decomposition, occurs all the time in the natural world. Organic material,
the remains of dead animals and plants, is broken down and consumed by micro-organisms and
eaten by small invertebrates. Under controlled conditions, however, the process can be speeded up.
Composting has many benefits;
It provides a useful way of reclaiming nutrients from organic refuse
Saves valuable landfill space and possible contamination of land and water due to landfill
‘leachate’
Can be used as fertiliser on farmland or in the garden
Improves the condition of soils
3